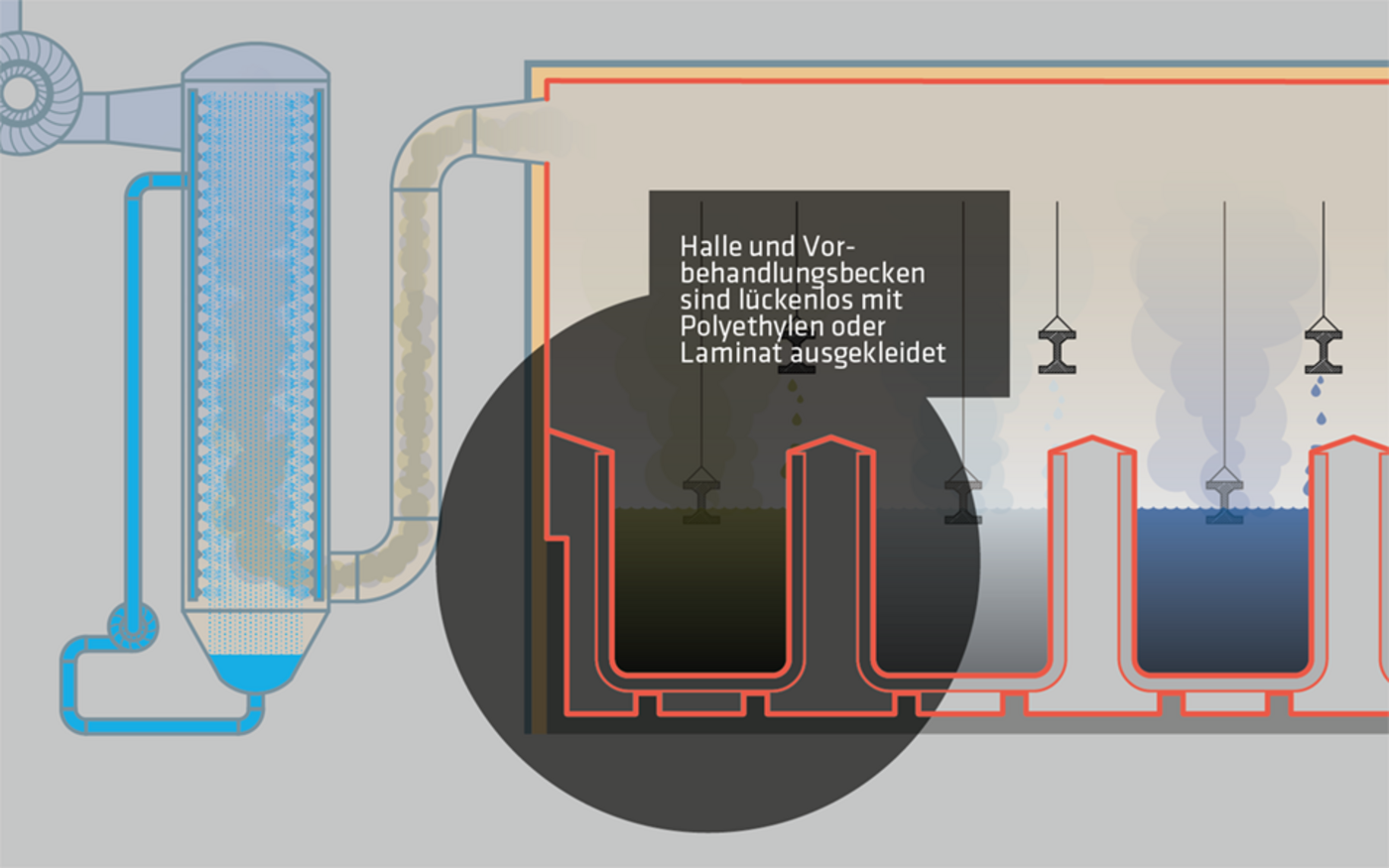
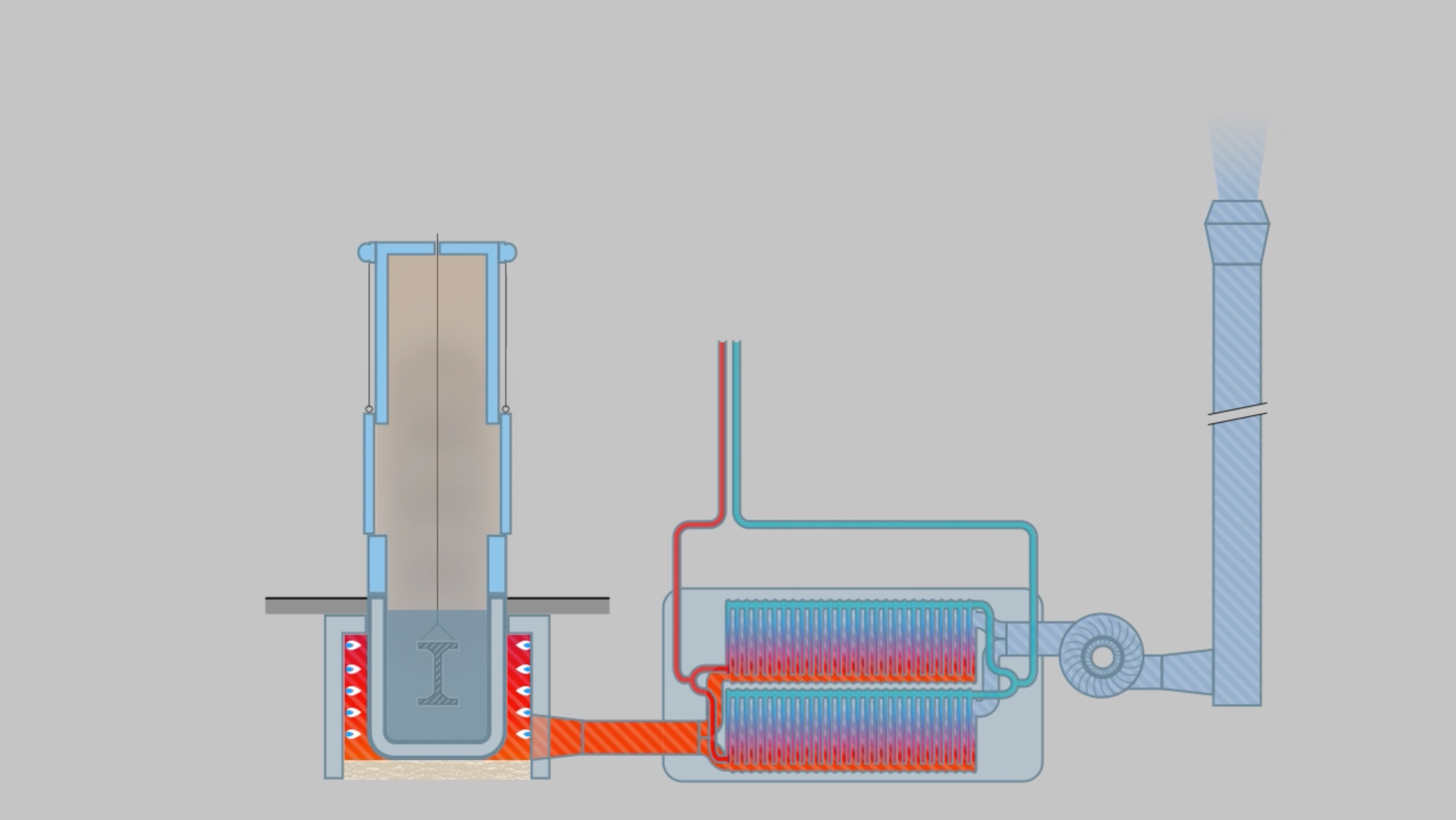
The animation shows the schematic sequence of hot-dip galvanizing and the associated air purification system.
The process steps in detail:
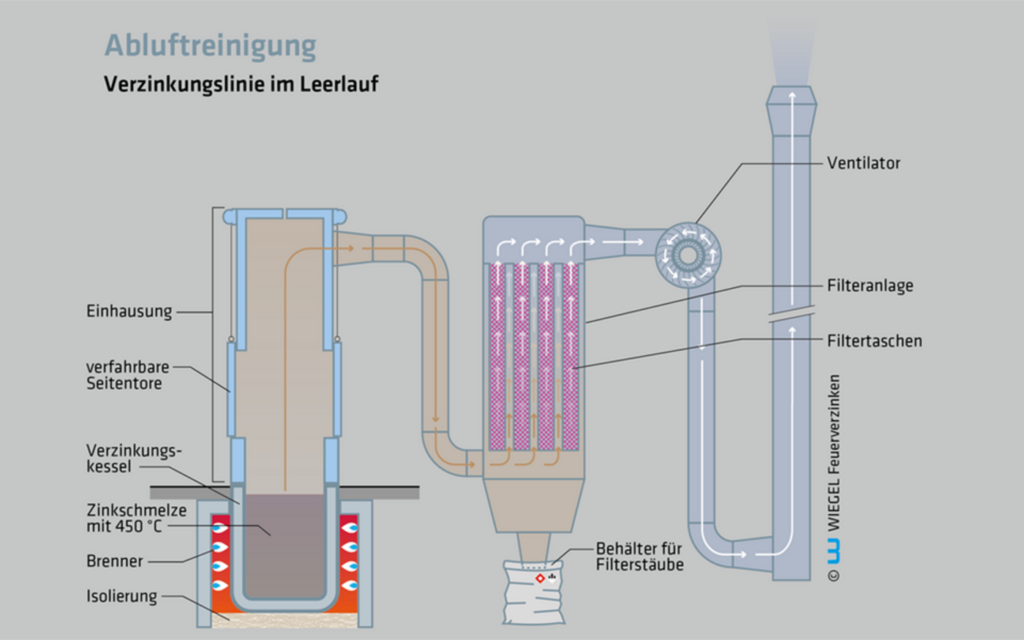
1. Galvanizing line at idle
Unladen zinc bath. Little dust and smoke development above the zinc bath.
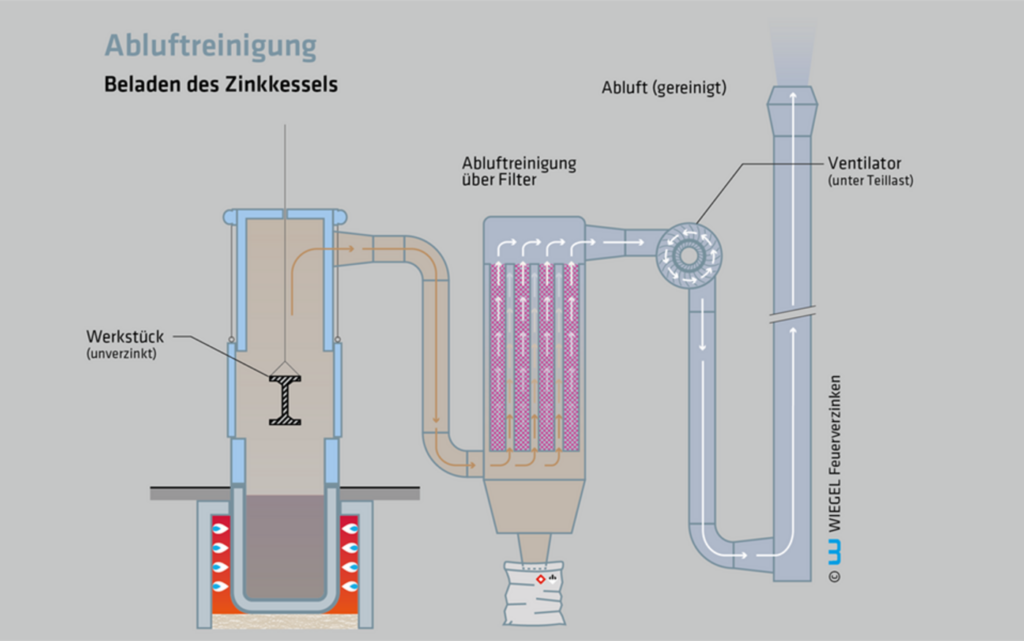
2. Loading of the zinc kettle
The workpiece is inserted into the housing at the top of the furnace.
3. Immersion of the workpiece
As the workpiece begins to be immersed in the zinc bath a lot of smoke and dust are produced and minute particles of metallic zinc can also splash up. The exhaust air over the zinc bath contains up to 1 g of particles per cubic metre. The exhaust system is running at full speed. The exhaust air is sucked through the filter at a very high volume flow rate.

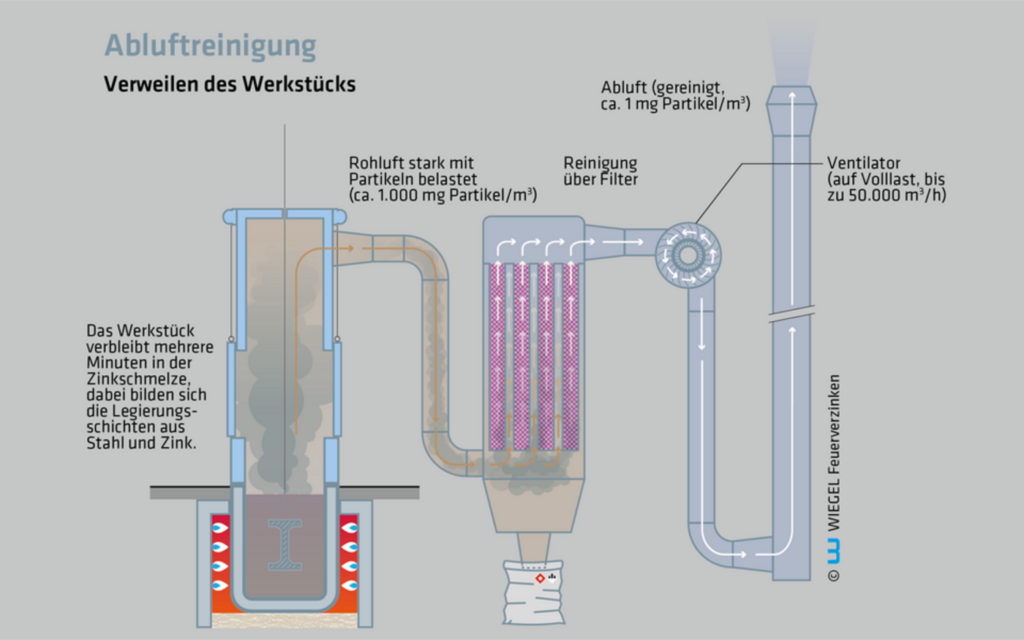
4. Lingering of the workpiece
While the workpiece is in the zinc bath the smoke and dust already starts to abate, but the exhaust system continues running at full speed.
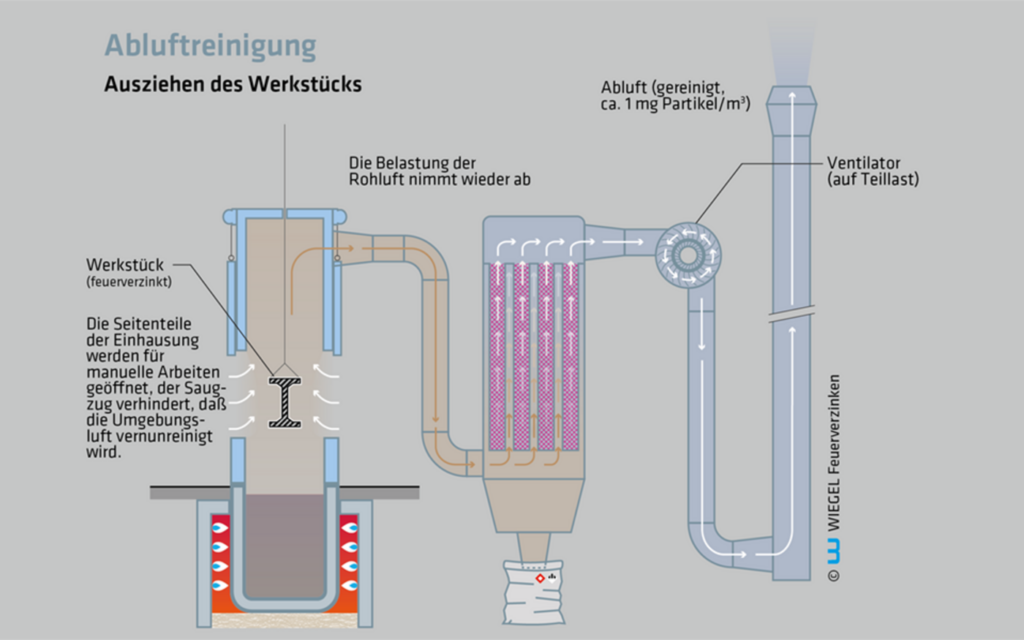
5. Pulling the workpiece out
To remove the oxides from the surface of the zinc bath and to perform other manual steps of the process the side walls of the housing need to be raised. Due to the strong draught, no pollutants enter the surrounding air.
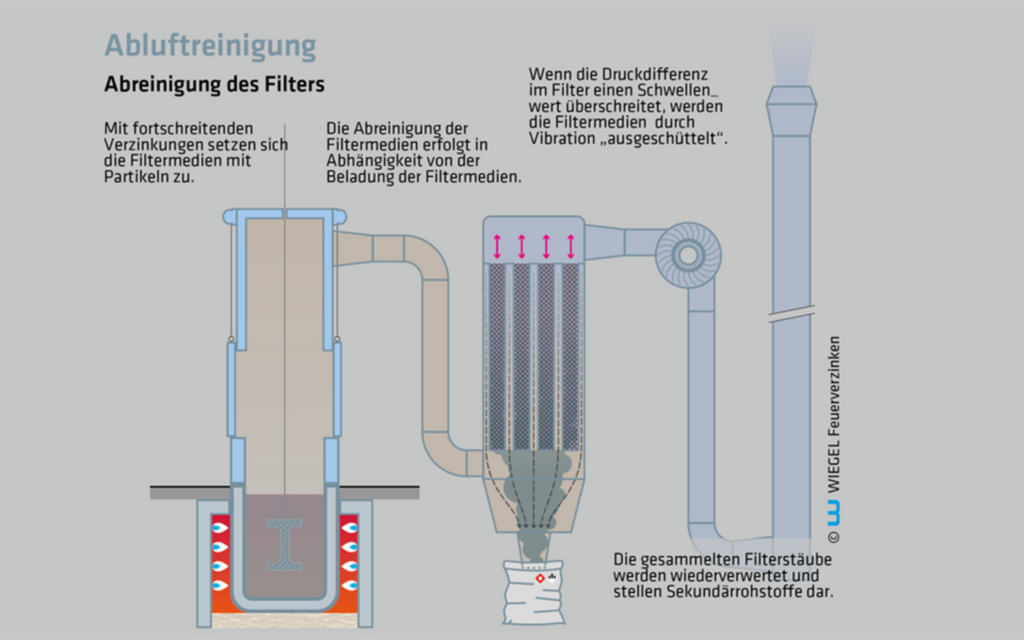
6. Cleaning the filters
Depending on the level of particulates produced during the galvanising process, the filter medium is flushed off periodically. The residues fall into a collection bin and are recycled.